The Essential Role of the Oil Pump in Diesel Engines
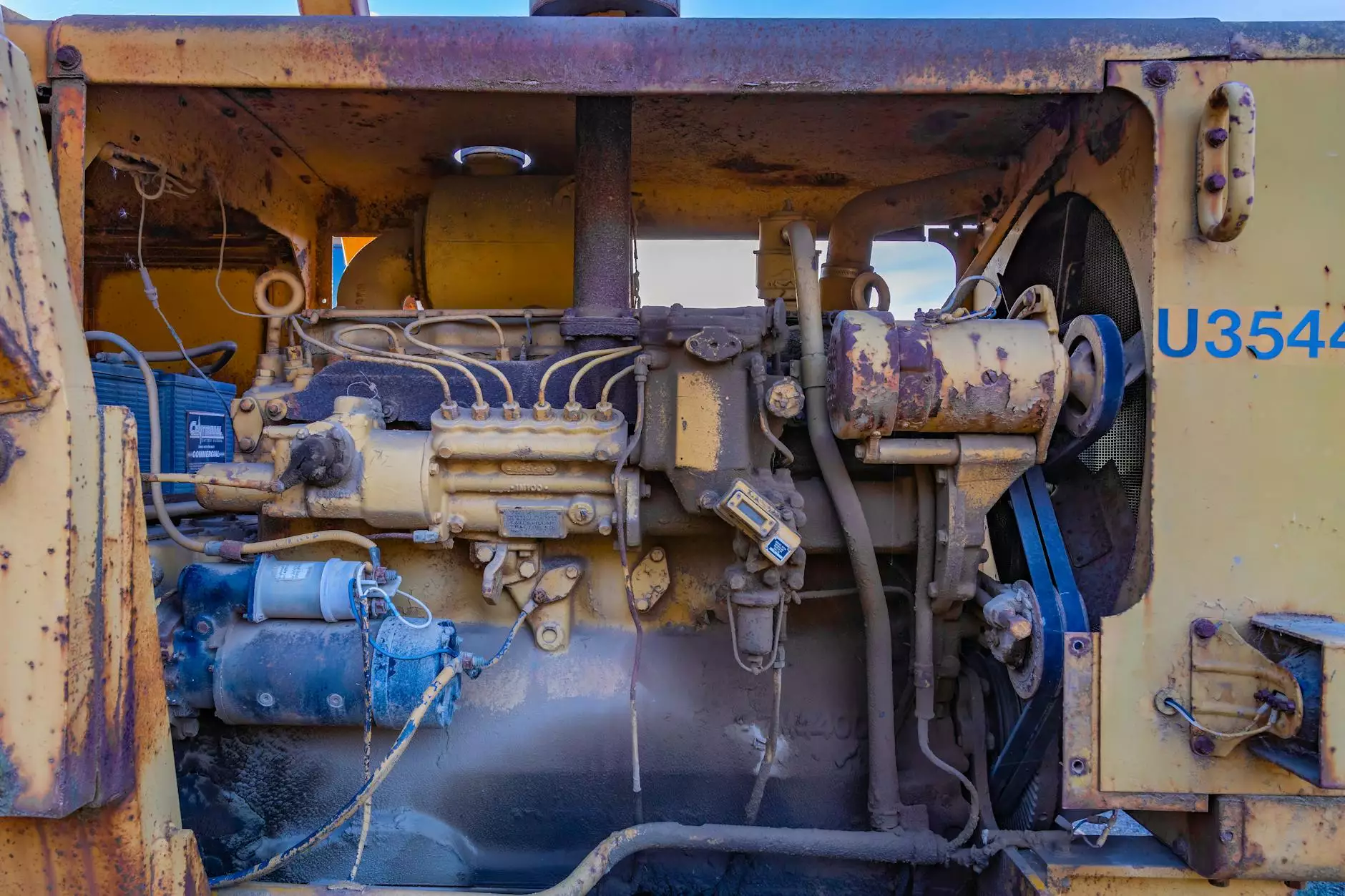

In the intricate world of diesel engines, the oil pump plays a pivotal role in ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Without adequate lubrication provided by the oil pump, diesel engines would suffer from excessive wear and tear, leading to a substantial decline in functionality and potential costly repairs. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the workings of the oil pump in diesel engines, exploring its significance, types, and maintenance tips, as well as its contribution to overall engine health.
Understanding the Diesel Engine and the Oil Pump
Diesel engines operate on a different principle compared to gasoline engines. They compress air to a high temperature and then inject diesel. This process demands high precision from all components, including the oil pump. The oil pump’s primary function is to circulate oil throughout the engine, ensuring that all parts are lubricated and protected from friction and heat.
How Does the Oil Pump Work?
The oil pump is driven by the engine’s crankshaft and works continuously to draw oil from the oil sump (or oil pan) and deliver it through various passages to critical components like bearings, pistons, and camshafts. Here's how it functions:
- Oil Pickup: The pump draws oil through a screen to prevent debris from entering.
- Pressurization: The oil is then pushed through the pump, creating pressure that allows for its distribution throughout the engine.
- Distribution: Pressurized oil flows to various engine parts where lubrication is vital.
- Return Cycle: After lubricating the components, the oil returns to the sump, and the cycle repeats.
The Importance of the Oil Pump in Diesel Engines
The oil pump is critical for several reasons:
- Prevention of Engine Wear: Continuous lubrication protects moving parts from friction, which can cause wear and potentially catastrophic engine failure.
- Heat Dissipation: The oil also helps in cooling the engine by carrying away heat generated by combustion.
- Contaminant Removal: Oil circulates through filters that trap debris and contaminants, preventing them from damaging sensitive components.
- Sealing: Lubrication creates a seal between moving parts, which enhances performance and efficiency.
Types of Oil Pumps in Diesel Engines
There are primarily two types of oil pumps used in diesel engines:
1. Gear Oil Pumps
Gear oil pumps are the most common type found in diesel engines. They feature two gears that mesh together to draw in oil and force it out under pressure. This design is robust and efficient, making it suitable for high-pressure applications.
2. Vane Oil Pumps
Vane pumps use a rotor with sliding vanes to create a vacuum that pulls oil in and pushes it out. These are less common in diesel engines but can be found in some applications where variable flow is needed.
Common Issues with Oil Pumps
Like any mechanical component, oil pumps can encounter issues that may compromise engine performance:
- Worn Gears: Over time, the gears in a gear pump can wear down, reducing oil pressure.
- Clogs: Over time, debris can clog oil passages, leading to insufficient lubrication.
- Seal Failures: Oil leaks can occur if the seals around the pump fail, reducing oil pressure and causing potential damage.
Signs of a Failing Oil Pump
Identifying issues early can prevent severe engine damage. Here are some warning signs of a failing oil pump:
- Low Oil Pressure Warning Light: This is the most obvious indicator. If your dashboard lights up, it’s a cause for concern.
- Engine Noise: If you hear increased engine noise or knocking sounds, it may indicate inadequate lubrication.
- Overheating: Consistent overheating can be a sign that the oil pump is not supplying enough oil.
Maintenance Tips for the Oil Pump
Regular maintenance is essential to the health of the oil pump and diesel engine. Here are some key maintenance tips:
- Regular Oil Changes: Changing the oil according to the manufacturer’s recommendations ensures that the oil pump remains effective and that contaminants do not build up.
- Check Oil Levels: Regularly check the oil levels and top off as needed to prevent the pump from running dry.
- Inspect Filters: Replace oil filters as needed to maintain proper oil flow.
- Monitor Engine Performance: Keep an eye on engine performance indicators and address any anomalies immediately.
Conclusion
In summary, the oil pump in diesel engines is an indispensable component, ensuring that all moving parts are properly lubricated, thus preventing wear and tear, dissipating heat, and protecting the engine from damage. Understanding how this vital component works and its significance will enable diesel engine owners and operators to maintain their machines more effectively.
At client-diesel.com, we provide a wide range of diesel engine parts and spare parts to keep your diesel engine running at peak performance. Whether you need replacement pumps or other essential components, our products are designed to meet the highest industry standards. Ensure the longevity and reliability of your diesel engines with quality parts and regular maintenance!